写在开头:这是免疫学的第三个章节,主要介绍非特异性免疫,其中包括非特异性免疫的结构,补体系统,以及病原体的识别。
Write at the beginning: This is the third chapter of immunology. It mainly introduce the innate immunity, which includes the structure of innate immunity, the complement system, and the pathogen recognition.
~~~~~~~~~~
Anatomic barriers & Initial chemical defenses
-Epithelial surfaces provide the first barrier against infection.
-Epithelial cells and phagocytes can produce several kinds of antimicrobial molecules.
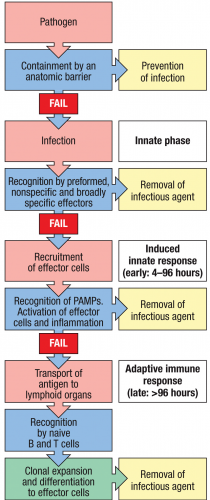
-Infectious agents must overcome innate host defence to establish an infection.
Mechanical, chemical, and microbiological barriers prevent pathogens from crossing the epithelia and colonizing tissues.
Antimicrobial molecules
–Lysozyme digests the cell walls of bacteria.
–Defensins are peptides that disrupt the cell membranes of microbes.
–Cathelicidins and RegIII lecticidins are examples of other antimicrobial molecules.
Complement system is a system of plasma proteins that mark pathogens for destruction.
Stages of complement action: Pattern-recognition trigger → Protease cascade amplification → Inflammation, Phagocytosis, Membrane attack
There are three pathways of the complement system, including lectin pathway, classical pathway, and alternative pathway. The same result of them is to coat microbial surfaces with C3b.
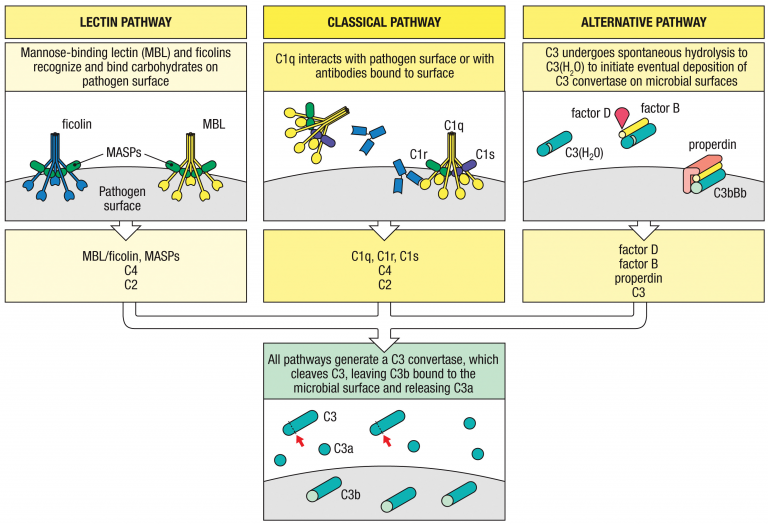
The lectin pathway uses soluble receptors that recognize microbial surfaces to activate the complement cascade.
1. Mannose-binding lectin (MBL) and ficolins form complexes with several serine proteases, MASP-1, MASP-2, and MASP-3, and recognize particular carbohydrates on microbial surfaces.
2. Activated MASP-2 on MBL or ficolin cleaves C4 to C4a and C4b, which binds to the microbial surface.
3. C4b then binds C2, which is cleaved by MASP-2 to C2a, forming C4b2a complex, and C2b.
4. C4b2a is an active C3 convertase cleaving C3 to C3a and C3b. C3b will then bind to microbial surfaces.
5. The C4a and C3a left function as inflammatory mediators to recruit immune cells.
The classical pathway is initiated by activation of the C1 complex and is homologous to the lectin pathway.
1. C1 complexes bind to the constant regions of antibodies on microbial surfaces. C1r on the complex will cleave and activate C1s.
2. Activated C1s cleaves C4 to C4a and C4b, which binds to the microbial surface.
3. C4b then binds C2, which is cleaved by MASP-2 to C2a, forming C4b2a complex, and C2b.
4. C4b2a is an active C3 convertase cleaving C3 to C3a and C3b. C3b will then bind to microbial surfaces.
5. The C4a and C3a left function as inflammatory mediators to recruit immune cells.
The alternative pathway is an amplification loop for C3b formation that is accelerated by properdin in the presence of pathogens.
1. C3b deposited by the classical or lectin pathway can bind factor B.
2. MASP-3 cleaves pro-factor D to form the active factor D.
3. Bound factor B is then cleaved by factor D into Ba and Bb, forming C3bBb complex.
4. C3bBb is an active C3 convertase cleaving C3 to C3a and C3b. C3b will then bind to microbial surfaces.
Spontaneous C3 hydrolysis can also activate the alternative pathway.
1. C3 may undergo spontaneous hydrolysis to C3(H2O), which binds to factor B, allowing it to be cleaved by factor D to form C3(H2O)Bb.
2. C3(H2O)Bb complex is a C3 convertase cleaving C3 to C3a and C3b. C3b will then bind to microbial surfaces.
3. Factor B can further bind to C3b on microbial surfaces to process alternative pathway.
C5 convertases are formed when C3b binds the C3 convertases C4b2a or C3bBb to form C4b2a3b or C3b2Bb.
C5 binds to C3b in these complexes, and is cleaved by the active enzyme C2a or Bb to form C5b and the inflammatory mediator C5a.
-The production of C5b initiates the assembly of the terminal complement components.
Assembly of the membrane attack complex (MAC)
1. C5 triggers the assembly of C6, C7, forming C5b67 complex, and it binds to membrane.
2. C8 binds to the complex and inserts into the cell membrane.
3. C9 molecule s bind to the complex and polymerize.
4. About 10-16 c9 molecules will form a pore in the membrane, called the membrane attack complex (MAC).
Effects of the complement pathway activation
–Inflammatory response: Small fragments of some complement proteins, such as C3a and C5a can recruit immune cells to the infection site and promote inflammation.
–Phagocytosis: Phagocytes will engulf pathogens coated with complement receptors, like C3b.
–Lyse pathogens: The terminal complement proteins polymerize to perforate cell membranes.